C++ 是一种强类型语言,这意味着每个变量都必须有一个明确的数据类型。数据类型决定了变量可以存储的数据种类以及占用的内存大小。C++ 中的数据类型可以分为以下几类:
- 基本数据类型(Primitive Data Types)
- 派生数据类型(Derived Data Types)
- 用户定义数据类型(User-defined Data Types)
基本数据类型:
- 整型(Integer Types)
int:通常为 4 字节,表示整数。short:通常为 2 字节,表示短整数。long:通常为 4 或 8 字节,表示长整数。long long:通常为 8 字节,表示更长的整数。
- 浮点型(Floating-point Types)
float:通常为 4 字节,表示单精度浮点数。double:通常为 8 字节,表示双精度浮点数。long double:通常为 10 或 16 字节,表示更高精度的浮点数。
- 字符型(Character Types)
char:通常为 1 字节,表示单个字符。wchar_t:通常为 2 或 4 字节,表示宽字符。
- 布尔型(Boolean Type)
bool:通常为 1 字节,表示真(true)或假(false)。
2. 派生数据类型(Derived Data Types)
派生数据类型是基于基本数据类型构建的,主要包括:
- 数组(Array):存储相同类型元素的集合。
- 指针(Pointer):存储变量的内存地址。
- 引用(Reference):变量的别名。
- 函数(Function):表示函数的类型。
3. 用户定义数据类型(User-defined Data Types)
用户定义数据类型是由程序员自定义的数据类型,主要包括:
- 结构体(Struct):可以包含多个不同类型的成员。
- 类(Class):类似于结构体,但可以包含成员函数。
- 枚举(Enum):定义一组命名的整数常量。
- 联合体(Union):所有成员共享同一块内存。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 基本数据类型
int integerVar = 42;
short shortVar = 32767;
long longVar = 2147483647L;
long long longLongVar = 9223372036854775807LL;
float floatVar = 3.14f;
double doubleVar = 3.141592653589793;
long double longDoubleVar = 3.141592653589793238L;
char charVar = 'A';
wchar_t wideCharVar = L'B';
bool boolVar = true;
// 派生数据类型
int arrayVar[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 数组
int* pointerVar = &integerVar; // 指针
int& referenceVar = integerVar; // 引用
// 用户定义数据类型
struct Person {
std::string name;
int age;
};
Person personVar = {"Alice", 30};
enum Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE };
Color colorVar = GREEN;
union Data {
int i;
float f;
char c;
};
Data dataVar;
dataVar.i = 10;
// 输出变量值
std::cout << "int: " << integerVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "short: " << shortVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "long: " << longVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "long long: " << longLongVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "float: " << floatVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "double: " << doubleVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "long double: " << longDoubleVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "char: " << charVar << std::endl;
std::wcout << "wchar_t: " << wideCharVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "bool: " << std::boolalpha << boolVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
std::cout << arrayVar[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "pointer: " << *pointerVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "reference: " << referenceVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "struct: " << personVar.name << ", " << personVar.age << std::endl;
std::cout << "enum: " << colorVar << std::endl;
std::cout << "union: " << dataVar.i << std::endl;
return 0;
}代码解释
- 基本数据类型:定义了各种基本数据类型的变量,并初始化它们。
- 派生数据类型:定义了一个数组、一个指针和一个引用。
- 用户定义数据类型:定义了一个结构体
Person、一个枚举Color和一个联合体Data。 - 输出:使用
std::cout输出各个变量的值。
Sizeof
sizeof并不是库函数,sizeof 是 C++ 中的一个运算符,用于计算数据类型或变量所占用的内存大小(以字节为单位)。它可以用于以下场景:
- 计算数据类型的大小:例如
sizeof(int)。 - 计算变量的大小:例如
sizeof(variable)。 - 计算数组的大小:例如
sizeof(array)。
sizeof 返回的是一个 size_t 类型的值,表示占用的字节数。
实例代码
以下是一个使用 sizeof 打印上述所有数据类型占用空间的实例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 基本数据类型
int integerVar;
short shortVar;
long longVar;
long long longLongVar;
float floatVar;
double doubleVar;
long double longDoubleVar;
char charVar;
wchar_t wideCharVar;
bool boolVar;
// 派生数据类型
int arrayVar[5];
int* pointerVar;
int& referenceVar = integerVar;
// 用户定义数据类型
struct Person {
std::string name;
int age;
};
Person personVar;
enum Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE };
Color colorVar;
union Data {
int i;
float f;
char c;
};
Data dataVar;
// 输出各数据类型的大小
std::cout << "Size of int: " << sizeof(int) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of short: " << sizeof(short) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of long: " << sizeof(long) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of long long: " << sizeof(long long) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of float: " << sizeof(float) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of double: " << sizeof(double) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of long double: " << sizeof(long double) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of char: " << sizeof(char) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of wchar_t: " << sizeof(wchar_t) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of bool: " << sizeof(bool) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of array (int[5]): " << sizeof(arrayVar) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of pointer (int*): " << sizeof(pointerVar) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of reference (int&): " << sizeof(referenceVar) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of struct Person: " << sizeof(Person) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of enum Color: " << sizeof(Color) << " bytes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Size of union Data: " << sizeof(Data) << " bytes" << std::endl;
return 0;
}运行输出结果:
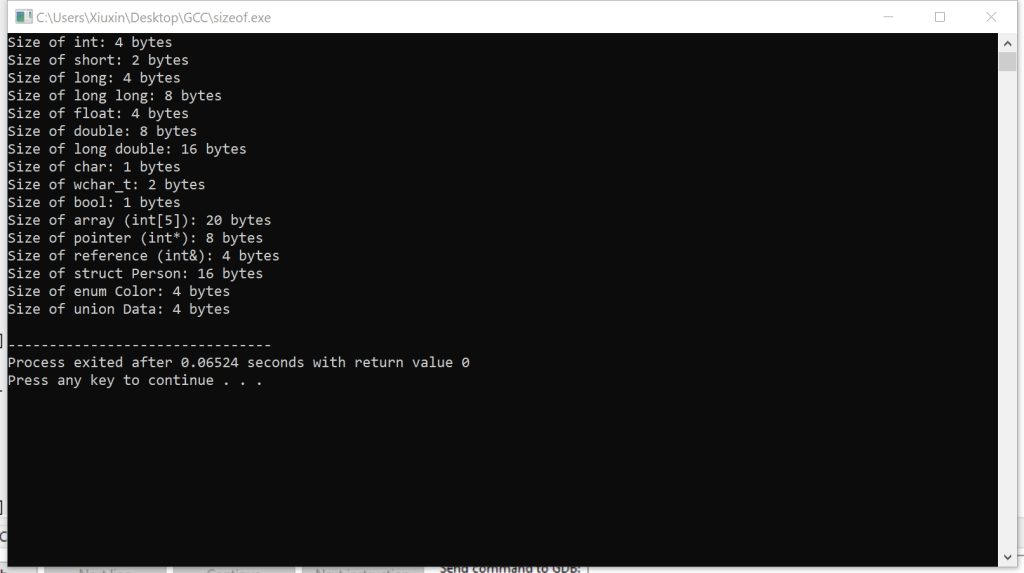
总结
sizeof是一个非常有用的工具,可以帮助我们了解数据类型或变量占用的内存大小。- 对于数组,
sizeof返回整个数组的大小(元素数量 × 每个元素的大小)。 - 对于指针和引用,
sizeof返回指针或引用本身的大小,而不是它们指向的对象的大小。 - 用户定义数据类型(如结构体、枚举和联合体)的大小取决于其成员的大小和对齐规则。
Comments NOTHING